Description
Carbohydrates formula for endurance sports athletes. 5-different times of glucose supply for up to 120 minutes of high energy output.
Glucose is especially useful for medium to high-intensity exercises that require sustained levels of activity. It can enable athletes to sustain performance at a high level for longer by delaying fatigue. This means that you can improve athletic performance by eating carbohydrates before and exercising.
Muscle glycogen, the predominant form of stored glucose in the body, and blood glucose are the main energy substrates for muscle contraction during exercise. Sucrose is an ideal substance for athletes to incorporate because it provides both glucose and fructose.
Therefore, it is essential that athletes monitor their diet to maintain and increase muscle glycogen deposits, since they are a major limiting factor of prolonged exercise performance. Carbohydrate-rich diets are also recommended for endurance and ultra-endurance exercise, because they are associated with increased muscle glycogen stores, as well as delayed onset of fatigue. In addition, high carbohydrate diets and carbohydrate intake before and during exercise have shown to be beneficial due to increased concentrations of hepatic glycogen and maintenance of blood glucose.
The effect of carbohydrate intake on athletic performance mainly depends on the characteristics of the exercise, the type and amount of carbohydrate ingested and the time of intake. A combination of these factors must be taken into account when analysing individual athletic performance.
Of course, not all types of sugars / carbs are the same.
Endurance Carbs 0′-120, combines a mix of 5 types of carbs with different molecular weights, absorption times, glycemic indexes, especially designed to support the athlete with glucose supply for 2 hours after consuming.
The key is the different glucose releasing times of these 5 types of carohydrates which Endurance Carbs 0′-120′ include.
| Ingredient | Per 100g | Per dosage (40g) |
| Endurance Carbs 0’-120’ multi-time releasing carbohydrates blend (Dextrose, Fructose, Maltodextrin, PalatinoseTM, Amylopectin) | 87.34 | 34.94 |
Dextrose:
WHAT IS DEXTROSE AND HOW IS IT USED AS A SPORTS SUPPLEMENT
Dextrose, a monosaccharide, is actually the dextrorotatory form of glucose. Carbohydrates are mainly classified as ‘simple’ or ‘complex’ carbohydrates. Being a simple monosaccharide, dextrose contains only one sugar molecule. Simple sugars cause a rise in blood glucose level very quickly; however, they are deprived of nutritional value.
Dextrose as a sports supplement
Recent researches have shown that dextrose, a fast absorbing simple sugar, could be influential in kicking athlete’s sports performance up a notch. ‘Glycemic index’ measure refers to the rate at which carbohydrate enters the bloodstream. Dextrose has a very high ‘glycemic index’ which means it is absorbed extremely fast. As far as health and fitness are concerned, if dextrose is used at a proper time, in conjugation with suitable supplements, it could stimulate post-workout recovery and muscle glycogen level to a great extent.
How does it work?
During training, our body uses glycogen as fuel. As dextrose is rapidly absorbed in the bloodstream, athletes and bodybuilders believe that this property can be helpful in increasing physical performance and post-workout-recovery. This is achieved by continuous transportation of nutrients, faster into the muscles.
Consumption of dextrose before, during or after the training boosts strength and endurance by providing ‘raw energy.’ In addition, it maximises the gains of a person by triggering the muscle repair process afterward. Dextrose aids in increased uptake of creatine, and amino acids like Beta Alanine, L-Arginine, L-Carnitine as well as L-Glutamine. However, the primary objective associated with dextrose, as a supplement, is to cause a spike in insulin levels of the body right after we train.
Dextrose induces an Insulin spike
Insulin is a hormone made by pancreatic cells of our body that allows the consumption of sugar (glucose) from carbohydrates present in food as well as its storage. Glucose is stored as glycogen in muscles by virtue of insulin for future use. Insulin retains the blood sugar level from getting too low (hypoglycemia) or too high (hyperglycemia).
Due to exercise, the glycogen level in our muscles is depleted, and our cells expand slightly. This expanded volume refers to the anabolic state to absorb more proteins, amino acids, and glycogen. This is known as ‘anabolic window’ which usually lasts no longer than one-hour post-workout. Use of dextrose spike insulin levels which serves as the transportation system for nutrients – typically from the bloodstream to muscles to begin the recovery of ‘starving muscles.’ The quick absorption of dextrose in bloodstream elevates insulin levels and thus kick-starts the post-workout recovery process.
Primary benefits of Dextrose supplements
The major benefits associated with dextrose supplements involve;
- Muscle Growth:
As mentioned earlier, dextrose enters the bloodstream quickly due to high ‘GI’ and results in the rapid increase of carrier hormone, i.e. insulin. Thus it allows the muscle cells to absorb nutrients at a faster rate to aid recovery.
- Replenishes Glycogen Levels:
Apart from the induction of insulin spike that will shuttle proteins and amino acids into the nutrient-depleted muscle cells, dextrose plays a role in replenishing glycogen levels as well. The more glycogen level, the more energy the body has.
Fructose – A super Carb for Athletes!
Effects of Fructose on Athletes
Fructose is a naturally-occurring sugar that’s found in many sports drinks and gels. So what are the effects of fructose on athletes?
Fructose is the sugar that’s naturally found in fruits. Sports drinks and gels that athletes frequently consume, contain it. Consuming this nutrient has demonstrated concrete effects, especially when we’re talking about athletes. So what exactly are the effects of fructose on athletes?
Metabolizing fructose
Your metabolism moves more slowly than glucose. This means that it’s not unheard of for it to cause certain types of gastrointestinal problems. However, fructose taken in small quantities in combination with glucose doesn’t slow down the absorption of fluids. This can be a big plus when we’re talking about the efficiency of hydrating.
Scientific literature shows that consuming fructose and glucose together can be beneficial for sports performance. One of the principal reasons is that it lowers feelings of fatigue.
Effect of pre-exercise fructose ingestion on endurance performance
Studies have shoen that fructose ingestion is of benefit before prolonged exercise, because it provides a carbohydrate source to contracting muscles without transient hypoglycemia and a depression of fat utilization, and thereby delays the fatigue.
MALTODEXTRIN FOR ENDURANCE ATHLETES
- Made up of chains of glucose molecules and has a high GI, meaning that energy is available quickly
- Oxidized quickly during exercise
- Reduce the risk of developing stomach complaints during prolonged exercise
The carbohydrate source in many energy drinks, is specifically selected maltodextrin. The particular size of molecule balances the amount of energy delivered versus how quickly it empties from the stomach. This means that you will feel the performance benefits of consuming a sport drink with maltodextrin faster with no stomach problems.
Maltodextrin together with fructose gives a carb mix of medium-time releasing glucose, perfect to maintain stable blood glucose levels during training which gives to the athlete a great endurance and performance boost.
Palatinose™ – Slow & Stable energy supply for 2 hours
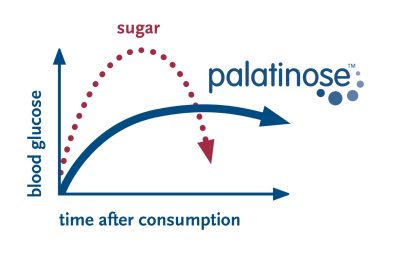
The only low-glycaemic carbohydrate providing balanced energy.
Nutritional benefits:
- Stretching the power curve: Enables balanced, sustained energy supply
- Supports a low glycaemic diet: Sugar levels – less is more
- Improved metabolism: Balanced carbohydrates in specialised nutrition
- Weight management: Promotes fat burning
- Dental health: Facilitates toothfriendly products
Amylopectin – A great intra training choice for high intensity workouts.
During the workout, Amylopectin will almost instantly recharge the energy that we use.
Consequently, it will improve our physical performance.
Trained athletes use around 2-3g of glycogen per minute.
Therefore, amylopectin is a good choice to carry out high-intensity activities.
Product Information:
800g | Lemon Flavour | 20 day supply
More flavours are coming until the end of 2021: Peach, Pineapple Coconut
Suggested use:
Mix 1 scoop (40g) to 300ml of room temperature water.
Consume the mix during your training, from your warm-up to the end of the training session.
You can use Endurance Carbs 0’-120’ during your carb-loading season or mix it to your protein shake after training for very faster recovery.
Ingredients: Dextrose, Fructose, Maltodextrin, PalatinoseTM (isomaltulose), Amylopectin (corn starch), Silicon Dioxide (anti-caking agent), Flavour, Lemon Powder (citrus limon, fruit), Dicalcium Phosphate, Magnesium Carbonate, Citric Acid, Sucralose, Colour (E-102)
Note: Supplements with high concentration in active ingredients and no preservatives, may turn from powder form to solid form. This is a natural effect of ingredients which are extra sensitive in humidity. Try to consume the product 20-30 days after opening. Keep in a dry and cool place always with the lid well closed. Do not use wet hands or tools to take the scoop from inside the tube.

*This website is for your education and general health information only. The ideas, opinions and suggestions contained on this website are not to be used as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis or treatment from your doctor for any health condition or problem. Users of this website should not rely on information provided on this website for their own health problems. Any questions regarding your own health should be addressed to your own physician. Please do not start or stop any medications without consulting with your doctor. We neither encourage you to do so, nor can we be held responsible for the fall out of failing to seek the counsel of a medical health practitioner.










